The semiconductor manufacturing industry generates highly complex wastewater containing hydrofluoric acid (HF), nitric acid (HNO₃), sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄), and alkaline cleaning agents, as well as heavy metals (Cu, Ni, Al, Zn) and fine particles of silica, SiC, photoresist, and slurry residues.
These waste streams are produced from etching, CMP polishing, photoresist stripping, and equipment cleaning processes, and require treatment systems offering exceptional chemical resistance, high precision, and long-term stability.
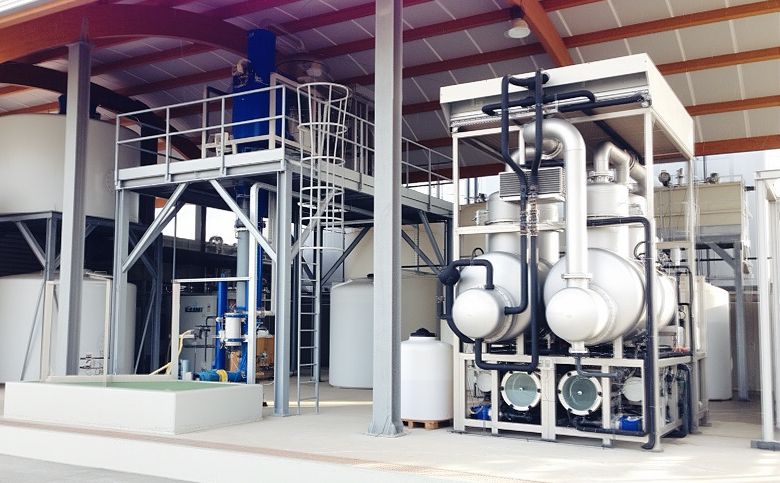
Deepflow provides high-purity wastewater treatment systems tailored for semiconductor fabs, wafer manufacturing, and IC packaging facilities.
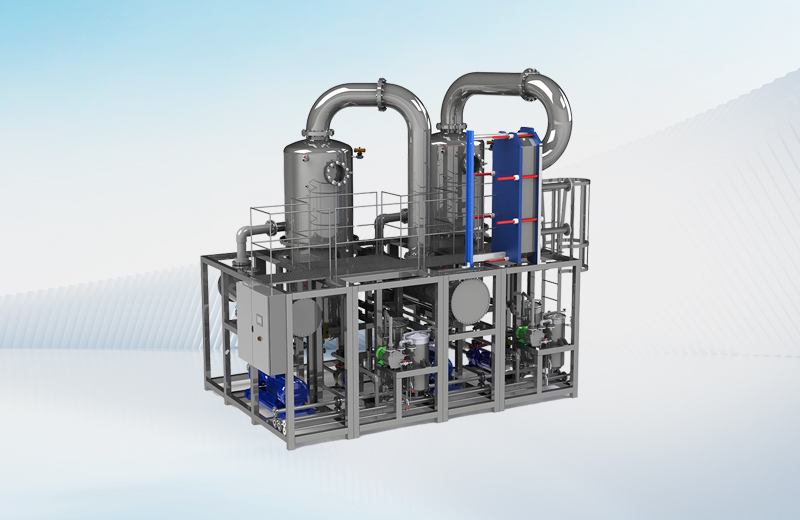
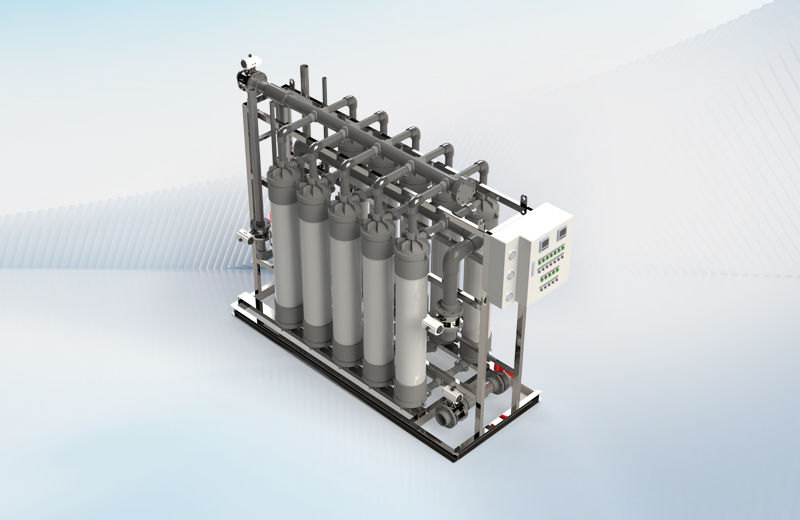
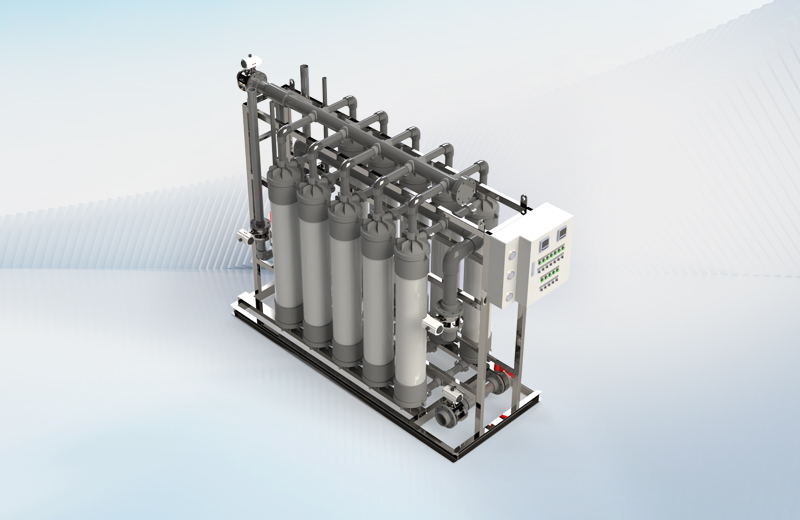
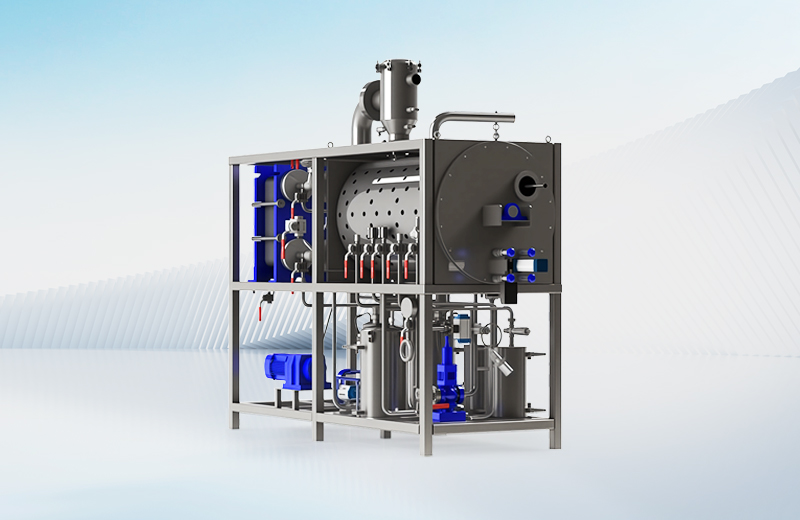
Our modular systems integrate RaeX neutralization and chemical precipitation, Seltra ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis, and Aevya or PFET evaporation to achieve reliable removal of pollutants and recovery of ultrapure water.
For facilities requiring Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD), Vorkx crystallizers and RedGan dryers are incorporated to recover high-purity salts and minimize solid waste.